The Winter Solstice

REASON FOR THE SOLSTICE
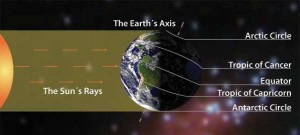 In astronomy, the solstice is either of the two times a year when the Sun is at its greatest distance from the celestial equator, the great circle on the celestial sphere that is on the same plane as the earth’s equator. In the Northern Hemisphere, the winter solstice occurs either December 21 or 22, when the sun shines directly over the tropic of Capricorn; the summer solstice occurs either June 20 or 21, when the sun shines directly over the tropic of Cancer. In the Southern Hemisphere, the winter and summer solstices are reversed.
In astronomy, the solstice is either of the two times a year when the Sun is at its greatest distance from the celestial equator, the great circle on the celestial sphere that is on the same plane as the earth’s equator. In the Northern Hemisphere, the winter solstice occurs either December 21 or 22, when the sun shines directly over the tropic of Capricorn; the summer solstice occurs either June 20 or 21, when the sun shines directly over the tropic of Cancer. In the Southern Hemisphere, the winter and summer solstices are reversed.
The winter solstice marks the shortest day and the longest night of the year. The sun appears at its lowest point in the sky, and its noontime elevation appears to be the same for several days before and after the solstice. Hence the origin of the word solstice, which comes from Latin solstitium, from sol, “sun” and -stitium, “a stoppage.” Following the winter solstice, the days begin to grow longer and the nights shorter.
PAGAN HERITAGE
Winter Solstice has been celebrated in cultures the world over for thousands of years. This start of the solar year is a celebration of Light and the rebirth of the Sun. In old Europe, it was known as Yule, from the Norse, Jul, meaning wheel.
Today, many people in Western-based cultures refer to this holiday as “Christmas.” Yet a look into its origins of Christmas reveals its Pagan roots. Emperor Aurelian established December 25 as the birthday of the “Invincible Sun” in the third century as part of the Roman Winter Solstice celebrations. Shortly thereafter, in 273, the Christian church selected this day to represent the birthday of Jesus, and by 336, this Roman solar feast day was Christianized. January 6, celebrated as Epiphany in Christendom and linked with the visit of the Magi, was originally an Egyptian date for the Winter Solstice.
Many of the symbols of Christmas echo its aspect of rebirth and hope in darkness. Holly was thought to be important because it retains its greenery right through the winter months, and as such is a symbol of summer life in the winter starkness. Holly was the male symbol of this greenery, and Ivy was the feminine, the two often placed together as a symbol of fecundity at the dark end of the year. There was also a belief that evergreen plants and trees were refuges for the woodland spirits through the winter months.
Solstice Dates ...
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer Solstice | 21 June 2010 | 21 June 2011 | 20 June 2012 | 21 June 2013 | 21 June 2014 | 21 June 2015 |
| Winter Solstice | 21 Dec 2010 | 22 Dec 2011 | 21 Dec 2012 | 21 Dec 2013 | 21 Dec 2014 | 22 Dec 2015 |






