Going Underground – The Story of the London Tube
 In 2013 the London Tube celebrated it’s 150th anniversary. The London Underground, or Tube as it is known in Britain, was the first of its’ kind in the world. Thanks to this seminal invention modern cities can sustain and transport millions of people everyday far and beyond what their ‘natural’ capacity would ever have been with out it. It’s all the more remarkable because it wasn’t even an Engineer who thought of it and laboured to see it all happen.
In 2013 the London Tube celebrated it’s 150th anniversary. The London Underground, or Tube as it is known in Britain, was the first of its’ kind in the world. Thanks to this seminal invention modern cities can sustain and transport millions of people everyday far and beyond what their ‘natural’ capacity would ever have been with out it. It’s all the more remarkable because it wasn’t even an Engineer who thought of it and laboured to see it all happen.
The Idea
On the Friday January 9th. 1863 London went underground. Work on the world’s first underground railway started in 1860 when the Metropolitan Railway began building a tunnel more than three miles long from Paddington to Farringdon Street. It was largely financed by the City of London, which was suffering badly from horse-drawn traffic congestion that was having a damaging effect on business. The idea of an underground system had originated with the City solicitor, Charles Pearson, who had pressed for it for years. It was he who persuaded the City Corporation to put up money and he was probably the most important single figure in the underground’s creation. Unfortunately he died in 1862, only a few months before his brainchild came to life.
The First Line
The first section linked the City with the railway stations at Paddington, Euston and King’s Cross, which had been built in the previous 30 years. The chief engineer was John Fowler, the leading railway engineer of the day, who would go on to create the Forth Bridge in Scotland. He did not come cheap and his Metropolitan Railway salary of £137,700 would be worth about £10 million today.
A deep trench was excavated by the ‘cut and cover’ method along what are now the Marylebone Road and the Euston Road and turning south-east beside Farringdon Road. Brick walls were built along the sides, the railway tracks were laid at the bottom and then the trench was roofed over with brick arches and the roads were put back on top, although the last stretch to Farringdon was left in an open, brick-lined cutting. Stations lit by gas were created at Paddington, Edgware Road, Baker Street, Great Portland Street, Euston Road and King’s Cross on the way to Farringdon, which was at ground level. William Gladstone, who was later to become Prime Minister but who was Chancellor of the Exchequer at the time, and his wife Catherine were passengers on a trial trip in May 1862.
Built round the clock by shifts of navvies, the line had to avoid numerous water and gas pipes, drains and sewers. There was even a problem when the noxious Fleet Ditch sewer flooded the works in Farringdon Road, but all that was dealt with and on January 9th, 1863 the line’s completion was celebrated at a gathering of railway executives and some 600 guests. Members of Parliament and City grandees including the lord mayor all started off from Paddington and were carried in two trains along the line to Farringdon Street station, where a banquet was held, speeches made and due tribute paid to the memory of Charles Pearson. Music was provided by the Metropolitan Police band.
The line was opened to the public on the following day, a Saturday, and people flocked to try it out. More than 30,000 passengers crowded the stations and pushed their way into packed trains. The underground had been mocked in the music halls and derisively nicknamed ‘the Drain’. There were predictions that the tunnel’s roof would give way and people would fall into it, while passengers would be asphyxiated by the fumes, and an evangelical minister had denounced the railway company for trying to break into Hell.
In fact the railway was a tremendous success and The Times hailed it as ‘the great engineering triumph of the day’. In its first year it carried more than nine million passengers in gas-lit first-class, second-class and third-class carriages, drawn by steam locomotives that belched out choking quantities of smoke. The fact that the passengers were at first forbidden to smoke in the carriages was not much help.
More Lines
Over the next two years the line was extended further east into the City to Moorgate and, in the other direction, to Hammersmith. Other lines were soon added to the growing network, deeper underground tunnelling was introduced and the steam trains were replaced by electric trains. The first underground electric railway, the City and South London, which ran from near the Bank of England under the Thames to the South Bank, opened in 1890. It was the first line to be called ‘the tube’ and the windowless carriages with their heavily upholstered interiors were popularly known as ‘padded cells’.
As far as the City was concerned, the corporation was able to sell its shares in the Metropolitan Railway at a profit and the underground did ease congestion for a time. A more lasting consequence was to make commuting far easier and so cause London to sprawl out even more from its centre, while the number of people actually living in the City itself declined sharply.
London Tube Construction Photo Gallery
- Pioneering excavation under residential houses during the construction of the Metropolitan Railway extension to South Kensington in 1866.
- Illustrated London News engraving showing the 1st stages of construction of the Metropolitan Railway, King’s Cross, 1862
- William Gladstone with directors and engineers of the Metropolitan Railway Company
- The Farringdon Station Banquet
- Another example of Cut and Cover
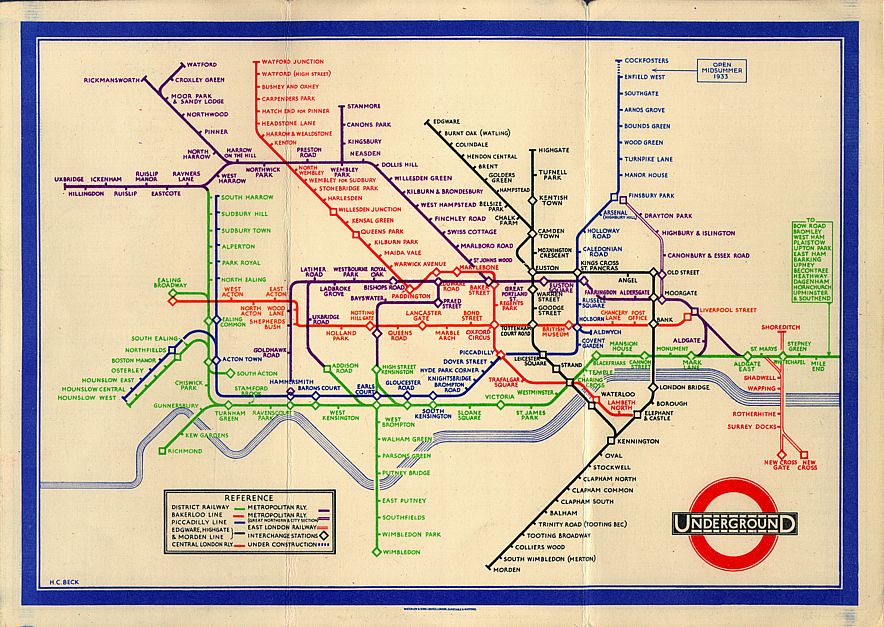
The Iconic London Tube Map
Up until 1931 all tube maps had been based on rel life topography, that is it mapped the actual geographical and physical layouts of the lines and stations
The first diagrammatic map of London’s rapid transit network was designed by Harry Beck in 1931. Beck was a London Underground employee who realised that because the railway ran mostly underground, the physical locations of the stations were irrelevant to the traveller wanting to know how to get to one station from another — only the topology of the railway mattered. This approach is similar to that of electrical circuit diagrams












You must be logged in to post a comment.